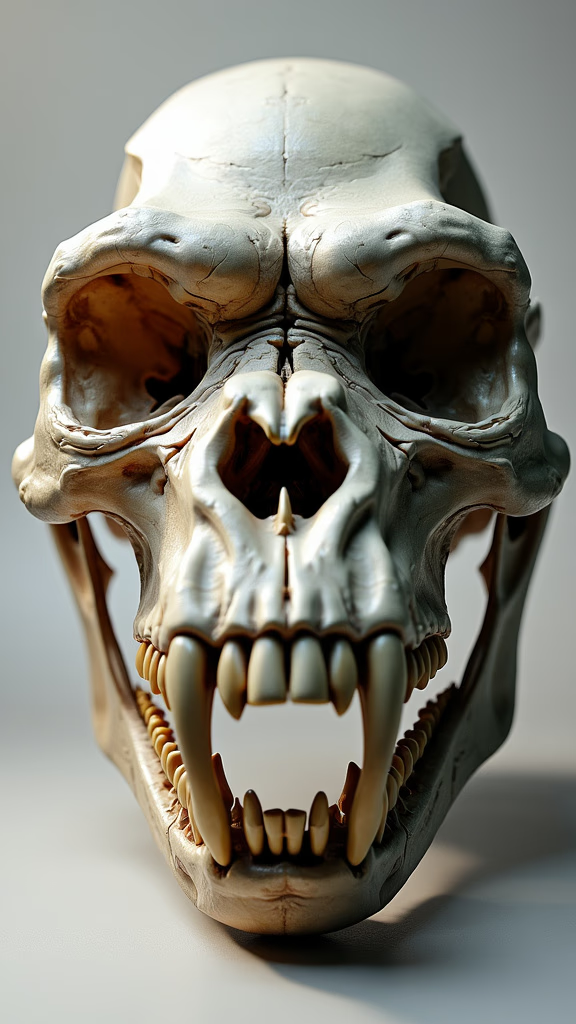
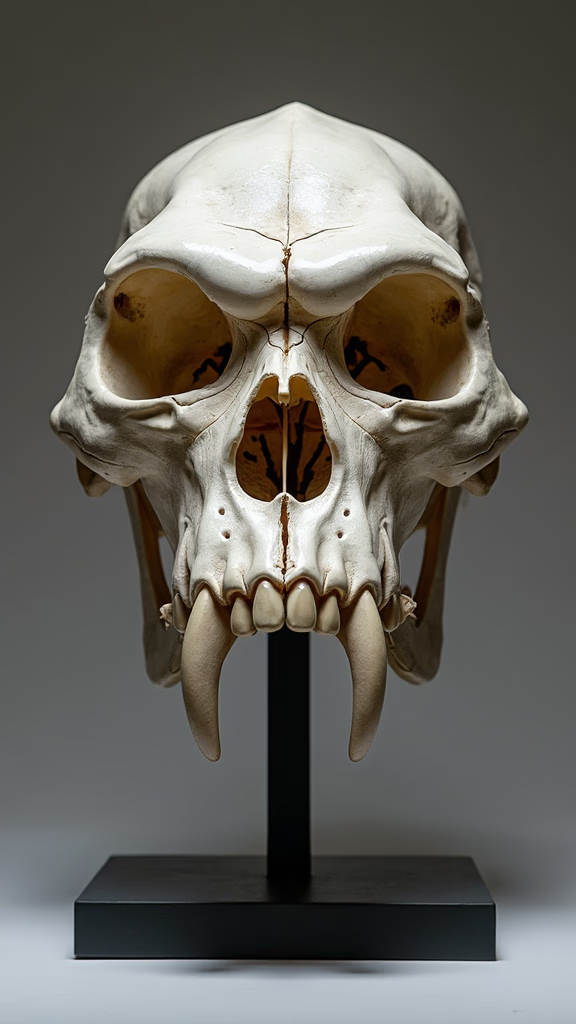
Gorilla skulls are fascinating structures that reveal much about their owners’ lives and habits. The prominent brow ridge and large jaw muscles are adaptations for their herbivorous diet. Studying these features helps us understand how gorillas have evolved to thrive in their environments.
The large nasal openings of gorilla skulls are another striking feature. These allow for a strong sense of smell, crucial for locating food and navigating their dense forest habitats. By examining these skulls, we gain insights into the sensory world of gorillas.

The size and shape of a gorilla’s skull can vary significantly between males and females. Male gorillas typically have larger, more robust skulls with pronounced sagittal crests. These distinctions help researchers identify gender and age in fossil records.
Gorilla skulls provide a window into the past, allowing scientists to trace evolutionary changes over time. Fossilized skulls help piece together the story of how modern gorillas came to be. Each skull tells a tale of adaptation and survival.

The dental structure of gorilla skulls is adapted to their diet of leaves, stems, and fruit. Their large molars are perfect for grinding tough vegetation. Examining these teeth can give us clues about their dietary habits and food availability in their habitats.
Gorilla skulls have large, powerful jaws to support their chewing needs. These jaws can exert tremendous force, necessary for breaking down fibrous plant material. Understanding these adaptations helps explain how gorillas sustain themselves in the wild.

The study of gorilla skulls can also shed light on their social behavior. The size and shape of certain skull features can indicate dominance and social hierarchy within groups. These physical traits often correlate with behavioral patterns observed in the wild.
Gorillas use their strong jaws and teeth not only for eating but also in displays of aggression or dominance. The robust nature of their skulls supports these activities. By studying these aspects, we can better understand the social dynamics of gorilla troops.

Comparing gorilla skulls with those of other primates can highlight unique evolutionary paths. Unlike smaller primates, gorillas have evolved distinct features that support their larger body size and ground-dwelling lifestyle. These comparisons help us appreciate the diversity within the primate family.
The differences in skull morphology between gorillas and other primates are a testament to their diverse evolutionary pressures. Each species has adapted to its environment in unique ways. Studying these differences enriches our understanding of primate evolution.

The cranial capacity of gorilla skulls provides insights into their brain size and cognitive abilities. While not as large as human brains, gorilla brains are adapted for complex social interactions and problem-solving. Analyzing skull size helps researchers make inferences about their intelligence.
Gorilla skulls also show adaptations for strong neck muscles, necessary to support their massive heads. These muscles are crucial for their posture and movement. Understanding these physical traits helps explain how gorillas navigate their arboreal and terrestrial habitats.

The structure of a gorilla’s skull can provide information about their sensory capabilities. Large eye sockets suggest keen vision, essential for their forested environments. This visual acuity aids in foraging and detecting predators.
Gorilla skulls also have well-developed ear structures, indicating good hearing. This is important for communication and staying alert to potential threats. By studying these features, we gain a fuller picture of their sensory world.

Gorilla skulls show significant variation between different subspecies. Western and eastern gorillas, for example, have distinct cranial features that reflect their different habitats and lifestyles. These differences are key to understanding the diversity within the species.
The skulls of mountain gorillas, a subspecies of eastern gorillas, are particularly robust. This adaptation helps them survive in their harsh, mountainous environment. By comparing these skulls, scientists can track how different environments shape physical traits.

Gorilla skulls are also valuable for understanding developmental stages. Juvenile and adult skulls show clear differences, reflecting growth and maturation processes. These changes provide insights into the life history of gorillas.
The study of gorilla skulls can reveal health and diet-related issues. For instance, wear patterns on teeth can indicate age and dietary habits. This information is critical for conservation efforts, as it helps predict the needs of gorilla populations.

Gorilla skulls are a crucial tool for forensic analysis in wildlife crime investigations. They can help identify poached individuals and determine the cause of death. This application underscores the importance of preserving these majestic creatures.
Understanding the anatomy of gorilla skulls aids in veterinary care and rehabilitation. Knowledge of skull structure is essential for diagnosing and treating injuries or illnesses. This expertise contributes to the well-being and conservation of gorilla populations.
Here is the rest of the gallery: